Forest resources and context of Democratic Republic of the Congo
According to the 2018 study conducted by FRMi, the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) had around 114.5 million hectares of forest in 2017, representing 49% of the total land area.
Another study by the FAO in 2020, counts 126 million hectares of forest (including degraded forests)

Land surface
226.7million ha
Forest cover
126million ha (2020)
Production forest
19.7million ha
Forest ownership
100% publicly
Forest resources in DRC
Types of forest
The DRC Forest Code (2002) distinguishes three categories of forests:
- Forêts Classées (classified forests), such as Nature reserves, Fauna Reserves, Recreational Forests and National Parks – public domain: these forests are often called ‘protected areas’, but shouldn’t be mistaken with the next category of protected forests. The forests have been defined by an classification act and have juridical limitations on user rights and exploitation, based on their ecological values. Classified forest shall make out at least 15% of the total DRC territory.
- Forêts protégées (protected forests) are those that are not defined by a classification act and they have less restrictions on user and exploitation rights. Protected forests can be part of a concession contract, for a term not exceeding 25 years. Also, a local community can obtain concession rights on the protected forest, for a part or the total area, when the community has customary rights on that forest. (Examples are the artisanal logging permit and harvesting permit).
- Forêts de production permanente (permanent production forests) are subtracted from the protected forests, by public inquiry. The Forest Code’s regulations on exploitation apply. Forest concessions and Local community forest are examples of permanent production forests.
Only about 10% of the DRC's forests are currently allocated for logging.
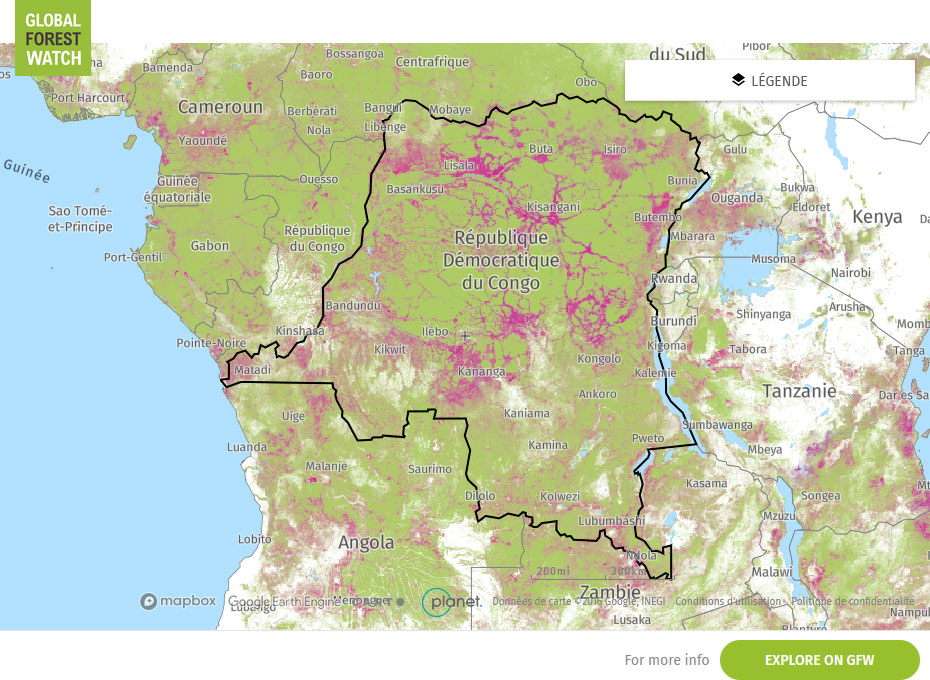
DRC’s forests cover closed high rainforests, open forests and woody savannah. The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is part of Africa’s Congo Basin, together with Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea and Gabon. DRC is the most biologically diverse country in Africa and one of the most important centres of biodiversity in the world, encompassing over half of Africa’s tropical forest. Overall, the DR Congo is known to have more than 15,000 plant and animal species, including 450 mammals, 1,150 birds, 300 reptiles and 200 amphibians, and more than 3,200 endemics such as the okapi, Congolese peacock, and bonobo (WWF-DRC). Mountains and high plains are at the eastern border with Uganda and Rwanda, including the Virunga National Parc, home of the famous mountain gorilla.
Although the deforestation rate is relatively low compared with that of many other tropical countries (-0.83% over the last 10 years), it represents an area of over 1 000,000 ha per year in the case of this vast country. It is among the highest deforestation figures in the Congo Basin and is rising. Main drivers of deforestation in DRC are slash and burn agriculture, uncontrolled bushfires, charcoal production for local and regional markets, cattle ranching, and, last but not least: illegal (artisanal) logging.
Forest ownership in drc
The forest legislation (2002) divides the national forest territory into a public domain and a private domain of the state. (Verifor, 2008).
key figures
| Land surface | 226.7 million hectares |
|---|---|
| Forest cover | 126 million hectares (55%) |
| Production forest | 19.7 million hectares designated for production |
| Forest ownership | 100% publicly owned |
| Annual change rate | -0.83% per year between 2010 and 2020 |
Source: FAO, 2015
See also: Global Forest Ressources Assessment 2020, FAO