Forest resources and context of Central African Republic
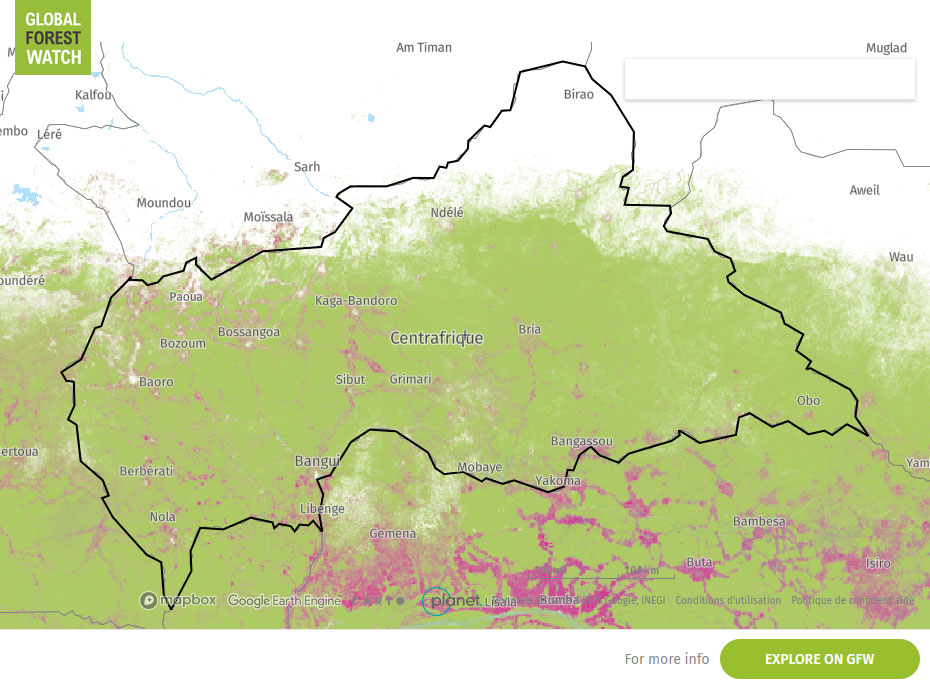
44.6% of CAR's total area of dense humid forests are used for production purposes.
Land surface
62.3million ha
Forest cover
22.2million ha
Production forest
4.8million ha
Forest ownership
98.9% publicly
Forest resources in Central African Republic
Types of forest
The forests of the Central African Republic (CAR) can be distinguished in the dense humid rainforest in the south and north of these forests a dryer transition zone between forest and savannah. About 90% of the nation is covered with more or less dense wooded and shrubby savannas. The dense humid rainforests of the south-west and, to a lesser extent, the Bangassou region, which are mainly semi-deciduous, cover over 3 million hectares and only 5.5% of the nation. The forest production areas are exclusively located in the south-west's dense forest massif. From an economic standpoint, this semi-deciduous forest is one of Africa's richest. In addition to a relatively high density of Sapelli (Entandrophragmacylindricum), and other Meliaceae, there are significant concentrations of Ayous (Triplochytonscleroxylon) and Fraké (Terminaliasuperba). (Dacryodesbuettneri);
Out of a national area covering 62.3 million ha, CAR has nearly 6.9 million hectares of dense forests. In relation to the Congo Basin's total forests, though, CAR accounts for only 3.71%.
In the Central African Republic, since 1996, armed movements have been located in the north of the country (Ouham-Pendé, Ouham and Vakaga prefectures), i.e. several hundred kilometres from the forest production region.
Forest ownership in Central African Republic
Almost the whole forest area (98.9%) belongs to the state.
The Central African forest law (2008) splits the national forest domain into two parts: the permanent forest domain (the south-west massif, the Bangassou massif and the savannas) and the non-permanent forest domain (public authorities' forest areas, private individuals' forests and community forests).
key figures
| Land surface | 62.3 million hectares |
|---|---|
| Forest cover | 22.2 million hectares (35.6%); mostly naturally regenerated forest |
| Production forest | 4.8 million hectares designated for production |
| Forest ownership | 98.9% publicly owned 1.1% privately owned |
| Annual change rate | -0.1% per year; over the past 25 years (1990-2015) |
Source: FAO, 2015
See also: Global Forest Ressources Assessment 2020, FAO